Navigating the Complex Interplay of Privacy and Data Security in Computing
As IBM states, “Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption or theft throughout its entire lifecycle. It’s a concept that encompasses every aspect of information security from the physical security of hardware and storage devices to administrative and access controls, as well as the logical security of software applications.”
In increasingly digital computing, “privacy” and “data security” have become integral to discussions about technology and information management. These two concepts are often intertwined yet carry distinct meanings and implications. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricate relationship between privacy in computing and explore why they matter more than ever.
Privacy vs. Data Security: Understanding the Difference
Before we dive deeper into the relationship between privacy and security, let’s clarify their definitions:
- Privacy: Privacy concerns an individual’s right to control their personal information. It protects sensitive data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or use. Privacy involves consent, transparency, and respecting individuals’ choices regarding the collection and use of their data.
- Data Security: This, on the other hand, primarily focuses on safeguarding data from breaches, theft, or unauthorized alterations. It encompasses various technical and procedural measures to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
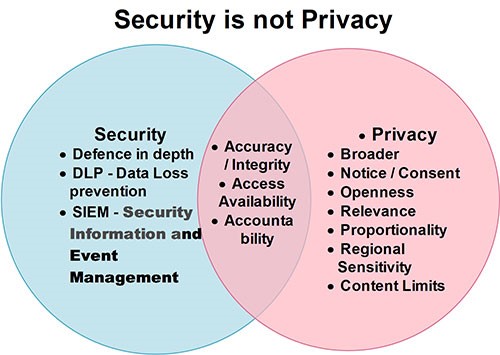
The Interplay between Privacy and Data Security
- Data Protection as a Privacy Pillar: Robust security practices are fundamental to protecting privacy. Data is not adequately secured, it becomes vulnerable to breaches, jeopardizing individuals’ privacy rights. Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA emphasize the importance of data security in ensuring compliance.
- Data Minimization: A fundamental privacy principle is data minimization, which advocates collecting only the data necessary for a specific purpose. Here, security plays a role in appropriately managing and protecting the collected data.
- Encryption as a Privacy Enabler: Encryption is a vital security measure that enhances privacy. When data is encrypted, even if accessed by unauthorized parties, it remains unreadable without the decryption key.
- Access Controls: Proper access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can access and handle sensitive data. This aligns with privacy principles that require consent and transparency regarding who can access one’s data.
- Incident Response and Notification: In case of a data breach, incident response protocols become crucial for data security and privacy. Timely detection and notification are necessary to mitigate harm and comply with privacy regulations.
Why Privacy and Data Security Matter
- Legal Compliance: Privacy laws and regulations require organizations to implement strong data security measures to defend individuals’ privacy rights. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties.
- Trust and Reputation: Data breaches erode trust and damage an organization’s reputation. People are less likely to trust companies with their data if they don’t believe their privacy is protected.
- Ethical Considerations: Beyond legal obligations, there’s a moral imperative to protect privacy. Respecting individuals’ privacy is a core principle of responsible technology use.
- Competitive Advantage: A strong commitment to privacy can be a competitive advantage. Consumers often choose companies that prioritize their data protection.
Wrapping up:
The connection between privacy and data security in computing is intricate and symbiotic. There is a very thin line that maintains our privacy. While they have distinct focuses, they are inseparable in practice. Organizations must recognize that safeguarding sensitive data is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a fundamental ethical responsibility and crucial to building trust with customers and users.
By integrating strong data security practices with a genuine commitment to privacy, businesses and technology professionals can steer the complexities of the digital landscape while respecting individuals’ rights and maintaining their integrity in the era of data-driven computing. For more insightful blogs, visit auxin.io.






