Ensuring Data Integrity: The Most Secure Methods
In today’s digital age, data is the lifeblood of corporations and organizations across the globe. Ensuring the integrity of this data is paramount. Data integrity refers to data’s accuracy, reliability, and consistency over its entire lifecycle. According to Varonis Data integrity refers to the reliability and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle. It can describe the state of your data—e.g., valid or invalid—or the process of ensuring and preserving the validity and accuracy of data. Error checking and validation, for example, are common methods for ensuring data integrity as part of a process
It’s about ensuring data remains unchanged and trustworthy, free from unauthorized alterations or corruption. With the increasing complexity of cyber hazards and data breaches, safeguarding data integrity has never been more critical. This blog will explore some of the most secure methods for ensuring data integrity.
What is the Difference Between Data Integrity and Data Security?
Data integrity and data security are two crucial aspects of managing and protecting data, but they focus on different aspects of data management and have distinct goals:
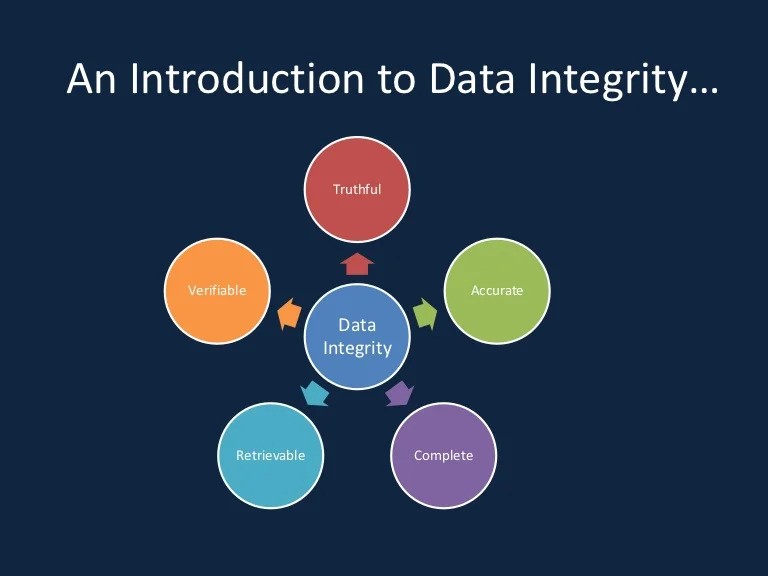
Data Integrity:
- Data integrity refers to data’s accuracy, consistency, and reliability throughout its lifecycle. It ensures that data remains unchanged and trustworthy at rest and during transmission or processing.
- Key components of data integrity include:
- Data is correct and free from errors or discrepancies.
- Data remains consistent and coherent over time and across different systems or databases.
- Data can be trusted to be authentic and valid.
- Data integrity mechanisms often involve checksums, hashing algorithms, error detection, correction codes, and data validation processes to detect and prevent data corruption or unauthorized alterations.
- Data integrity primarily focuses on maintaining the quality and reliability of data.
Data Security:
On the other hand, data security is a broader concept that encompasses protecting data from unauthorized access, disclosure, theft, or tampering. It focuses on safeguarding data against various threats and ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access and modify it.
Key components of data security include:
- Access Control: Implementing authentication and approval mechanisms to manage who can access and manipulate data.
- Encryption: Encrypting data at respite and in transit protects it from eavesdropping or theft.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Monitoring and detecting unauthorized access or malicious activities to prevent security breaches.
- Security Policies and Procedures: Establishing policies, procedures, and best practices for data handling and protection.
- Data security aims to preserve data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability (the CIA triad). It ensures that data is accurate and protected from security threats.
In summary, data integrity focuses on maintaining the accuracy and reliability of data, while data security focuses on safeguarding data from unauthorized access and other security threats. Both are essential for effective data management and protection, and they often complement each other in ensuring that data remains trustworthy and secure.
1. Encryption
Encryption is a cornerstone of data integrity. Encrypting data at rest and in transit confirms that even if a hostile actor gains access to your data, it remains indecipherable without the encryption keys. Advanced encryption standards like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) provides robust protection. Employing end-to-end encryption for sensitive data during transmission adds an extra layer of security.
2. Regular Backups
Frequent and automated backups are essential for data integrity. Backups should be stored securely, preferably offline or in isolated environments. Regularly test the restoration process to ensure your data can be recovered accurately in case of data loss or corruption.
3. Access Control and Authentication
Limiting access to data and systems is a fundamental security measure. Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure only authorized personnel can access and modify specific data. Robust authentication processes, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), bolster access security.
4. Data Validation and Verification
Implement data validation checks to ensure that incoming data meets predefined criteria. This helps prevent the introduction of erroneous or malicious data. Use checksums, hashing algorithms, or digital signatures to verify data integrity during transmission and storage. Any unauthorized changes will result in failed validation.
5. Data Auditing and Logging
Comprehensive auditing and logging mechanisms can help you monitor data access and changes. Keep detailed records of who accessed the data, when, and what actions they performed. Regularly review and analyze these logs for any suspicious activities.
6. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in industries where data integrity is paramount, like finance and healthcare. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without consensus from the network.
7. Security Updates and Patch Management
Regularly update and patch your software, operating systems, and applications to fix vulnerabilities that could be exploited to compromise data integrity. Staying up to date with protection patches is essential.
8. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
Consider deploying DLP solutions to monitor and prevent the unauthorized transfer or leakage of sensitive data. These tools can be configured to enforce policies that align with data integrity goals.
9. Employee Training and Awareness
Employees are often the weakest link in data integrity. Comprehensive training and awareness programs can educate staff about the importance of data security, safe data handling practices, and how to identify and respond to potential threats.
Wrapping up:
Data integrity is not just a compliance requirement; it’s a cornerstone of trust in the digital world. Employing a combination of these secure methods can help organizations ensure the integrity of their data.
Remember that data integrity is an ongoing process, and staying vigilant and proactive is vital to protecting your most asset your data. For more insightful blogs, visit auxin.io.






