Defending Against Phishing: Insights from T-Mobile, Viamedis, and France’s Cybersecurity Incidents
Introduction
In 2023, phishing attacks came to the forefront, affecting 23% of businesses, as indicated by Tech.co. The incidents involving T-Mobile in 2023, as well as Almerys and Viamedis, French healthcare payment service providers in February 2024, underscored the prominence of these cybersecurity threats.
These incidents underscore the critical importance of preventive measures, robust cybersecurity practices, and proactive strategies to fortify digital defenses against the escalating menace of phishing attacks. This blog explores the T-Mobile and French healthcare payment service providers’ data breaches and provides prescriptive guidance on preventing future attacks.
How do the Phishing Attacks work: The Top Threat in Data Breaches
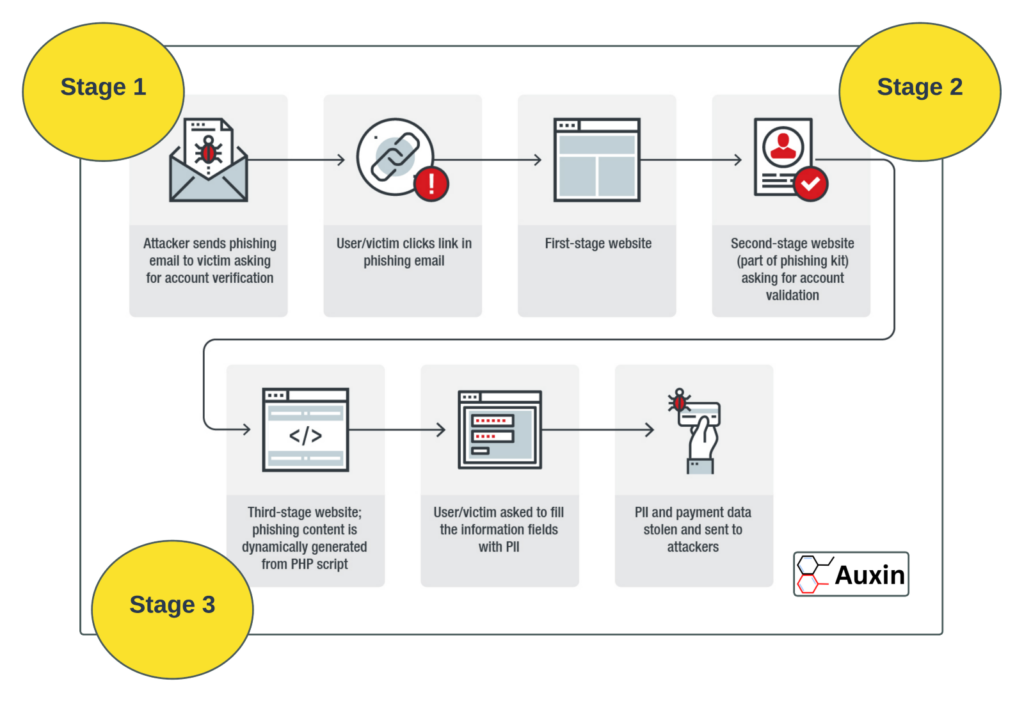
Phishing attacks are social engineering scams where attackers try to mislead you into revealing sensitive information or taking actions that benefit them. They often use emails, text messages, or phone calls that appear to be from a fair source, like your bank, credit card company, or even a friend. A typical attack looks like:
Stage 1: Attackers send phishing emails to the targeted person and ask for account verification. Then, the user clicks the provided link in a phishing email.
Stage 2: The victim opens the link, and the second website will ask for account validation.
Stage 3: The phishing content is automatically generated, and the user will be asked to fill in the information fields. Then, the personal information and payment data will be stolen and sent to attackers.
Phishing attacks have emerged as the foremost threat in data breaches, posing a substantial risk to individuals and organizations. This insidious method of cyber exploitation involves deceptive tactics to manipulate unsuspecting targets into disclosing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details.
In 2023, phishing attacks were the leading cause of data breaches, impacting 23% of businesses that reported experiencing a breach, according to a survey by Tech.co. These attacks can have significant consequences, compromising sensitive data, leading to financial losses, and damaging an organization’s reputation.
Case Studies
T-Mobile Data Breaches in 2023
As per Dark Reading, an extensively reported incident was the T-Mobile data breach the previous year, resulting in a staggering 37 million customers’ data, primarily allocated to customer payouts. Unfortunately, T-Mobile faced the brunt of two additional breaches in 2023, further jeopardizing customer data.
This intensifies the responsibility of businesses to fortify their networks, prioritize robust passwords among staff, and empower employees with the skills to identify the unmistakable indicators of phishing campaigns.
Devastating Impact of T-Mobile’s Data Breaches in 2023
- Customer information compromised: The January and April 2023 breaches compromised the data of 37 million and 836 customers, respectively. Exposed information included names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and account PINs.
- Increased risk of identity theft and fraud: This exposed information can be misused for fraudulent activities, like creating fake accounts, applying for loans, or making unauthorized purchases.
- Reputational damage: The repeated breaches eroded public trust in T-Mobile’s ability to protect customer data.
- Financial cost: T-Mobile potentially faced significant economic repercussions, including offering credit monitoring services, investigating the incidents, and facing lawsuits. This cost the company $350 million in 2022 – just in customer payouts.

Frence’s leading providers Data Breach (February 2024)
In February 2024, France experienced a significant data breach affecting nearly half its population. Two major healthcare payment providers, Viamedis and Almerys, were targeted in cyberattacks, compromising the personal information of over 33 million individuals.
InfoSecurity Magazine revealed this impactful data breach, impacting two major French healthcare payment service providers. These organizations play crucial roles in managing payments within the healthcare sector, serving millions of patients across France.
The potential compromise of such confidential and personal data raises serious concerns about privacy and security. Individuals impacted by the breach are at an increased risk of identity theft, fraudulent financial activities, and other malicious uses of their personal information. The exposure of Social Security numbers, addresses, and health insurance information adds a layer of severity to the breach, as this information is often used in targeted and sophisticated forms of identity theft and fraud.
The compromised data, still under investigation, is believed to encompass sensitive details like names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and health insurance information. The potential exposure of such confidential data raises serious concerns about privacy and protection for the affected individuals.

So, what is the Root Cause of Phishing Attacks
As per the Forbes Impact of Technology on the Workplace report, employees emerge as the vulnerability in business security, with data breaches in 2023 often stemming from phishing attacks and employee errors.
Despite these concerning patterns, the report reveals that 40% of businesses need to leverage essential cybersecurity tools. This article will delve into the critical cybersecurity statistics and preventions you can take to avoid such data breaches in 2024.
Auxin Preventions Guide
Auxin’s perspectives on preventive strategies align with the lessons derived from real-world cyberattacks like the T-Mobile and French healthcare payment providers’ data breaches. Delving into these strategies, we will explore how T-Mobile and French healthcare payment providers could have fortified their defenses from these data breaches.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Measures
- Investment in security infrastructure: Healthcare organizations, including payment service providers, must prioritize investments in robust cybersecurity solutions. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and data encryption technologies.
- Regular system updates and security patches: Consistent updates address known vulnerabilities in software and operating systems, minimizing the chances of exploitation by attackers.
- Data encryption: Implementing robust data encryption protects sensitive information, even if it’s breached.
User Awareness and Training
- Employee training programs: Regularly educate employees on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing email identification, password hygiene, and reporting suspicious activity.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all user accounts, adding a layer of security beyond passwords.
Data Minimization and Access Control
- Minimize data collection and storage: Only collect and store information necessary for legitimate business purposes.
- Implement access controls: Grant access to sensitive data only to authorized persons who require it for their job functions.
Incident Response Planning
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan: Cybersecurity incidents are a matter of “when,” not “if.” Therefore, security and risk management leaders must have a practical cybersecurity incident response plan that guides all aspects of incident management.
- Regular testing and review: Regularly update the incident response plan to ensure effectiveness.
Regulatory Compliance
- Ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations: This ensures data handling practices adhere to established legal requirements and contribute to a strong security posture. In simpler words, regulatory compliance keeps your business out of trouble.






