According to Gartner, account takeover (ATO) is a serious cybersecurity threat where attackers, posing as legitimate users, exploit stolen credentials to access sensitive accounts. This type of attack can be highly damaging as it allows unauthorized actors to gain control of personal or corporate accounts, posing as customers, employees, or other trusted users. The prevalence of these attacks has grown significantly, with 84% of organizations experiencing identity-related breaches in 2022 alone. Gartner’s findings also suggest that the impact of these breaches could have been minimized by adopting identity-centric security measures, indicating a critical need for organizations to prioritize and enforce robust identity and access management (IAM) frameworks.
A major challenge with ATO is that without technologies and policies like zero trust and multifactor authentication (MFA), identifying malicious account activity is difficult. This is because attackers can mimic legitimate users’ behavior, making it hard to detect suspicious logins, especially in organizations with weak or limited IAM systems. Unlike straightforward credential theft, ATO often goes unnoticed for longer periods, maximizing the damage caused. Organizations need to shift their focus from traditional network security to a more identity-focused approach, utilizing technologies that provide continuous authentication and authorization across all access points.
Cybercriminals employ various methods for account takeover, including phishing, brute force botnet attacks, and malware, and may acquire personal information from discarded mail or black-market purchases of “Fullz” — full sets of identifiable information. As online transactions and cloud applications continue to increase, so do opportunities for attackers. ATO risks are exacerbated by remote work, third-party vendors, and increasingly decentralized environments, making it essential for organizations to adopt stringent IAM practices that limit trust and demand explicit authentication for all users and devices accessing sensitive resources.
How Account Takeover Fraud Happens
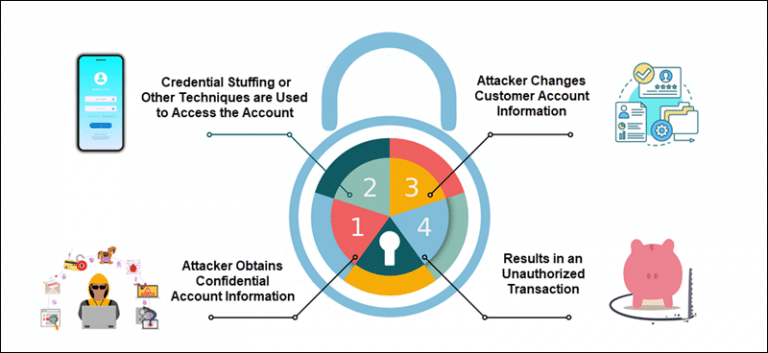
Account takeover (ATO) fraud occurs when a malicious actor gains unauthorized access to a user’s account, typically through stolen or otherwise compromised credentials. This form of fraud allows attackers to impersonate legitimate users, giving them access to sensitive data, the ability to make unauthorized transactions, and control over valuable accounts. Attackers often use sophisticated tactics to obtain access, which can bypass traditional detection systems if the organization lacks a robust identity and access management (IAM) strategy.
Here’s how ATO typically unfolds:
- Credential Theft: Attackers may obtain user credentials through phishing scams, social engineering, malware, or by purchasing “Fullz” (full profiles of identifying information) from the black market. With this information, attackers can mimic the behavior of legitimate users, making detection more difficult. Common techniques include phishing emails that trick users into disclosing passwords or using malware to capture keystrokes.
- Automated Attack Tools: Once credentials are acquired, cybercriminals often deploy automated tools like brute force bots or “checker” apps to validate login credentials across multiple accounts. These tools allow attackers to quickly test stolen credentials on a large scale, taking advantage of common password reuse among users. The automation of ATO attacks can overwhelm systems and enable attackers to gain access rapidly before defenses are triggered.
- Account Exploitation: With access granted, attackers can engage in a range of activities within the account. This might involve making unauthorized purchases, transferring funds, accessing sensitive data, or using the account for further fraudulent activities, such as sending phishing emails to contacts. The attack may go undetected for longer if the attacker is cautious and mimics the behavior of the legitimate account owner, allowing them to extract value without raising alarms.
These attacks are increasingly common due to the sheer volume of online accounts and the growing sophistication of cybercriminal techniques. Effective prevention strategies include adopting identity-centric security measures like zero trust, which assumes no implicit trust and continuously validates users and devices. Multifactor authentication (MFA), behavior-based detection, and stringent IAM policies are also crucial in identifying and mitigating ATO fraud risks.
Account Takeover Protection
Account takeover (ATO) protection involves a combination of security strategies and technologies designed to prevent unauthorized access to user accounts and protect sensitive information. Given the increasing sophistication of cybercriminal tactics, organizations need to implement a layered, identity-focused approach to safeguard against ATO fraud. Here are key protection methods to strengthen account security:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): A comprehensive IAM framework is critical in protecting against ATO. IAM solutions enforce access controls and help monitor user activity, making it easier to spot and respond to unusual login patterns. With centralized user management, organizations can set security policies, automate responses to suspicious activity, and manage user permissions across applications effectively.
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA): One of the most effective defenses against ATO, MFA requires users to verify their identity through multiple factors (e.g., a password, a mobile OTP, or biometric verification) before accessing an account. This approach adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to log in even if they have stolen credentials. MFA should be applied universally, especially for privileged accounts with access to sensitive data.
- Zero Trust Architecture: A zero-trust model assumes that every user, device, or application attempting to access an account is untrusted until verified. By continuously monitoring and verifying user identities and access requests, zero trust helps prevent unauthorized access, even from within the network. This architecture works well alongside technologies that enforce least privilege, granting users only the access necessary for their roles.
- Behavioral Analytics: Leveraging behavioral analytics can further enhance ATO protection by identifying anomalous actions that deviate from a user’s usual behavior. Machine learning algorithms can analyze login times, IP addresses, and user behavior to flag potentially malicious activity, triggering alerts or account locks when suspicious behavior is detected. This proactive approach helps catch attacks before they escalate.
- Security Awareness and Phishing Training: Since phishing remains one of the primary means of obtaining credentials, educating users on how to recognize and avoid phishing scams is crucial. Regular security training can help users identify malicious emails, links, and social engineering attempts, reducing the likelihood of compromised accounts.
With the rise in cloud adoption and remote work, ATO attacks are an increasingly prevalent threat. Implementing a multifaceted security strategy combining IAM, MFA, zero trust, and user training can greatly reduce the risk, protecting both individual accounts and overall organizational integrity.
Account Takeover Protection by Auxin Security
Auxin Security provides a robust suite of cybersecurity solutions that empower organizations to defend against account takeover (ATO) attacks by combining advanced identity and access management (IAM) tools with proactive monitoring and threat intelligence. Auxin Security’s platform is designed with a zero-trust framework at its core, enforcing continuous verification and limiting access based on precise user roles, which helps prevent unauthorized entry into sensitive accounts. By leveraging Auxin’s IAM features, organizations can centrally manage permissions, detect anomalies, and swiftly respond to potential account threats.
Auxin Security’s multi-layered approach incorporates machine learning-driven behavioral analytics to spot and address unusual activity in real time. These analytics provide deep visibility into user actions, flagging suspicious behavior patterns—such as logins from unusual locations or times—that often precede ATO fraud. By automating alerts and response workflows, Auxin helps security teams mitigate risks before they escalate, adding an additional safeguard against credential-based threats.
Additionally, Auxin’s identity-centric security solutions include multifactor authentication (MFA) integrations, making it easier for organizations to implement strong, seamless access controls across all user accounts. Auxin also offers tailored security awareness training modules, helping employees and end users identify and avoid phishing schemes and other social engineering attacks. With these comprehensive, integrated solutions, Auxin Security provides a powerful defense against ATO, ensuring both strong protection and adaptability for evolving cyber threats.






