How Do Honeypots Help You Secure a Network?
A honeypot is a specialized mechanism in cybersecurity network used to bait potential attackers towards a probing product, keeping them away from the legitimate product. This helps the organization gather information about existing system flaws and monitor the attack’s style, motivations, and goals.According to Forrester “A honeypot can be manufactured for any solution, including networks, software applications, and servers”. A honeypot is designed to resemble a legitimate product, including all the software, hardware components, and content structure.
Honeypots can also be termed decoy-based intrusion detection systems. Advanced attacks now require advanced technologies to deal with. Honeypots are now a famous tool for studying attack types and attacker behavior for enterprise security. The early detection mechanism of honeypots proved useful for cybersecurity professionals.
As your system cannot be tested against every possible attack, honeypots can help IT teams learn about new advanced attacks, trace them back to the source, and apply necessary protections over the actual product. The information gathered from this data collection process is of the utmost importance for identifying system flaws and liabilities. Hence, the security team knows where and how to improve the existing security protocols.
Use of honeypots in cybersecurity
The essential purpose of a honeypot is to look exactly like the software product you need to defend. E-commerce websites, payment software, and banking sites are the most sensitive services to be attacked. This is because, one, they got a large audience; two, susceptible information is stored on these sites; and thirdly, the financial details like bank account numbers and other information. A hacker will use financial information to retrieve or access your client’s data. Motivation for an attack can range from money, blackmailing, or any personal gain.
A honeypot may contain compromising information, including pictures and videos, to trap the criminal involved in ransomware attacks. A security analyst looks for three things while monitoring traffic in a honeypot, one, the source of the attack; two, the motivation for the attack and third, the mode of action. A honeypot may be placed outside an internal network to see the attack movement. Honeypot is a good cybersecurity practice that helps protect valuable software assets.
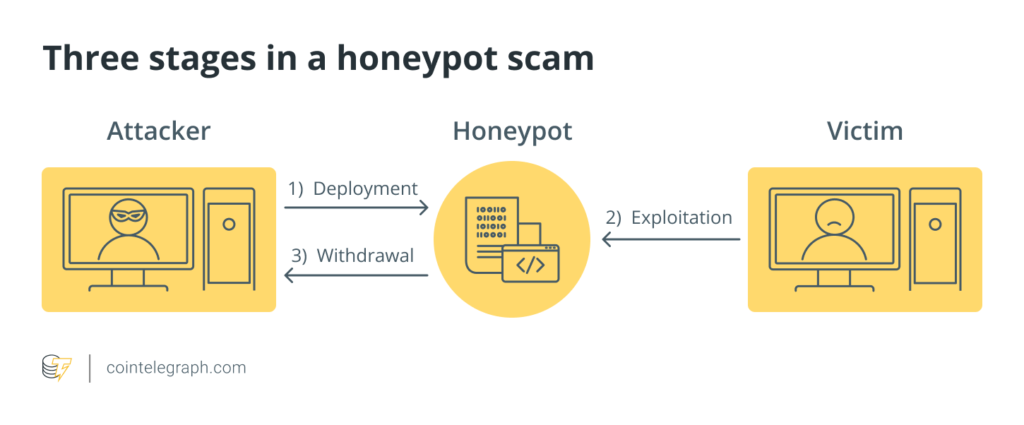
Types of Honeypots
Honeypots can be manufactured according to your system’s needs. There are many different types of honeypots used. Some of them are listed below:
Database Honeypot
A database honeypot is a decoy database used to lure attackers who focus on attacks like SQL injection or database manipulation. This honeypot will attract the cybercriminal to pass through some firewall to gain the trust and lets him launch an attack. An SQL injection attack can be traced through this, and the system can be protected.
Malware Honeypot
Malware Honeypot impersonates some software APIs and applications that gain the attacker’s attention. Any malware attack on such a system can be detected early and dealt with efficiently.
Spider Honeypot
Spider honeypots are malicious AI bots created to crawl through a network. They creep into a network and look for attackers who attack webpages and websites for session cookies and cookie details.
Benefits
Reliable Information: Instead of working on theories, try implementing every theoretical protection for your system. Installing a honeypot at your service and implementing security according to attack impacts and attacker motivations is better. This saves time and money as you don’t need to pay large security teams for hardware and software machinery you may not even need.
Reduced False Positives: False positive is a significant drawback; most alerts generated by a defense system are false. If these false positives are in large numbers, the network Using a honeypot saves you from getting these false positive alerts. This will gauge when and where you should put your efforts.
Surpass Encryption: As encryption using hashes is gaining popularity, large enterprises prefer encrypting their data files. Attackers also now use encryption-based attacks but do not worry about it anymore; using honeypots, all network traffic, including encryption, will be captured.
Conclusion
Everything comes at a cost; honeypots have their drawbacks, too, and being limited in the field of view is one of them. It’s program-dependent and cannot be used generically. They only capture the activity that comes in their direction and will not charge attacks other than that.
This is one reason security professionals do not recommend using honeypots instead of existing mechanisms. Instead, they see honeypots as a network and host-based invasion protection balancing technology.
Despite all this, the advantages of honeypots cannot be ignored. They brought a new sense to intrusion-protection solutions, especially now as honeypots are beginning to be deployed rapidly. It’s unfair to say that honeypots could quickly revolutionize the enterprise security domain. For more insightful blogs visit auxin.io






