Auxin Security guidance on how to manage ChatGPT Security risks
As with any new technology, there are inherent security risks associated with using ChatGPT, a large language model trained by OpenAI. According to a report by Gartner, “Organizations that leverage large language models for conversational AI need to understand and mitigate risks associated with the technology, including data privacy and security concerns.” Organizations can take several steps to manage these risks, including implementing robust access controls and monitoring, securing data transmission channels, and regularly conducting security assessments and penetration testing.
It is also essential to ensure that all employees are trained on using and handling ChatGPT and other conversational AI tools to mitigate the risk of insider threats. By taking a proactive and comprehensive approach to security, organizations can harness the power of ChatGPT while minimizing the associated risks.
Auxin Security understands that limiting technology is not an effective strategy. Instead, it is better to manage it. In the case of ChatGPT, it will be a complex task to block it effectively since it is part of daily user internet search engines. Auxin Security has drafted this initial document outlining the Chatbot architecture and high-level security guidance to manage the security risk as the technology matures commercially.
What is ChatGPT?
Any Chatbot at a very high level consists of the following steps
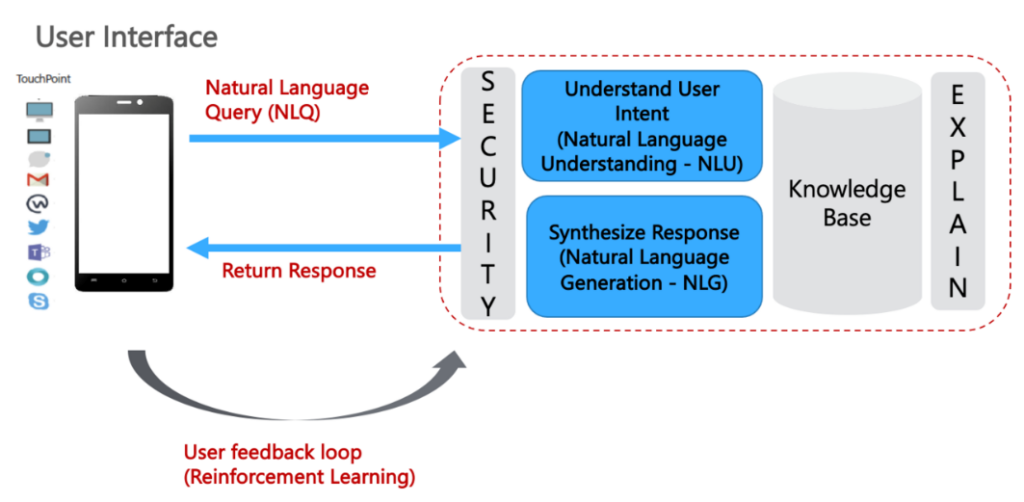
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Given a user query, first understand the user’s intent;
- Retrieve the relevant content from the underlying Knowledge base (KB);
- Natural Language Generation (NLG): Synthesize the answer and respond to the user;
- Retain the conversation context to answer/personalize any follow-up conversations.
- ChatGPT is a Large-scale language model created by OpenAI and launched in November 2022. It is built on top of OpenAI’s GPT-3 family of large language models and has been fine-tuned (an approach to transfer learning) using both supervised and reinforcement learning techniques.
- ChatGPT can answer a wide range of inquiries, engage in conversation, and produce text on a wide range of themes using the deep learning method GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer).
- ChatGPT is based on Generative Pre-Training by Open AI. The primary advantage of GPT models over others is the sheer volume of data on which they are trained. GPT-3: the third-generation GPT model, was trained on 175 billion parameters. GPT-3 thus acts as a pre-trained Large Language Model (LLM) that can be fine-tuned with very little data to accomplish novel NLP tasks, such as:
- Question-Answering (QA)/Chatbots
- Text extraction and summarization
- Auto-correct
- Translation
- Classification
- Natural Language Generation (NLG)
- One of the main improvements is that ChatGPT can carry out a continuous conversation. It remembers previous conversations and can replay them to the user.
Security Guidance
ChatGPT – General Security Guidance:
- Use Guidance: ChatGPT is not commercially mature since it lacks security controls, separation of data between users, and result verification – Auxin suggests it should not be used for any enterprise function or work-related activity.
- Employee Training: All employees, including contractors, should receive periodic security awareness training from firms to help them understand the value of safeguarding private company data and the dangers of disclosing it to third-party AI/ML applications and technologies, including ChatGPT chatbots.
Security best practices to avoid providing personal information or proprietary data as input to ChatGPT:
- Monitor usage: Firms can monitor how its employees use the network to detect attempts to give chatbots access to private data. Tune the existing DLP solutions to detect and block input data to OpenAI servers
- Implement access controls: The company can put access controls in place to stop employees from having unneeded access to important corporate data and sharing it with third-party chatbots.
Security best practices when using response/output generated by ChatGPT:
- Inaccurate/misleading information: Ensure that the responses generated are accurate and that the information provided is meaningful. Output from the ChatGPT cannot be used in documents, code, or systems. The information generated should be considered inaccurate and with possible commercial bias.
- Avoid chatbot-generated code: We can add security threats to a firm’s data, computing, and network. For example, terraform code generated by ChatGPT might have a malicious or known misconfiguration.
Conclusion
The business must balance safeguarding its systems and enabling employees’ productivity. Thus, it is advised to encourage employees not to utilize any ChatGPT technology for work purposes, implement network controls to block traffic, enable DLP solutions to detect data exfiltration specifically to OpenAI servers, and provide updated training to all employees.






