According to Gartner, phishing attacks remain a significant threat to organizations, exploiting vulnerabilities in human judgement. A notable example occurred in June 2022 when Twilio, a customer engagement platform, faced its second major breach. The attackers, known as the “0ktapus” hackers, used voice phishing techniques to impersonate Twilio’s IT department during a phone call. By deceiving an employee into thinking they were speaking to a legitimate representative, the hackers managed to obtain corporate login details.
This breach underscores the effectiveness of social engineering tactics in phishing attacks, as it led to unauthorized access to a limited number of customer contact details. It highlights the necessity for organizations to strengthen their security awareness training, ensuring employees can recognize and respond appropriately to potential phishing attempts. By enhancing employee vigilance and implementing robust security measures, companies can better protect themselves against these types of cyber threats.
The Growing Threat of Phishing Attacks: What You Need to Know
In the UK, phishing accounted for 83% of cyberattacks on businesses in 2022, highlighting its widespread impact. Globally, 323,972 internet users fell victim to phishing in 2021, with phishing responsible for half of all cybercrime incidents. Despite advanced security measures, such as Google blocking 99.9% of phishing attempts, cybercriminals still managed to steal $44.2 million, with an average loss of $136 per phishing attack. These attacks typically target victims through compromised email addresses, with nearly 1 billion emails exposed in 2021, affecting one in five internet users.
Given the rising tide of phishing attacks, particularly in sectors like financial services and law firms, it is crucial for businesses to adopt robust cybersecurity measures to protect their data and systems. With spear phishing campaigns favored by 65% of cybercriminal groups for intelligence gathering, businesses and individuals must remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their digital environments.
The Evolution of Phishing Attacks
Phishing methods have evolved, moving beyond emails to include text messages (known as “smishing”) and phone calls (“vishing”). Social media platforms have also become a common hunting ground for phishing campaigns, as attackers exploit the trust people place in friends and followers. As phishing tactics diversify, so does the range of potential victims—making it critical for everyone, from individual users to large enterprises, to be aware of the dangers and stay cautious.
One of the most dangerous forms of phishing is spear phishing, which involves highly targeted attacks. Unlike regular phishing, which casts a wide net, spear phishing focuses on specific individuals or organizations. Attackers often conduct detailed research on their targets, crafting personalized messages that appear legitimate. This makes it more challenging for victims to recognize the scam, increasing the likelihood of success. A 2019 study revealed that spear phishing was the most popular method of attack for 65% of cybercriminal groups, with intelligence gathering being their primary goal.
Why Phishing Persists: Leaked Emails and Dark Web Markets
A major reason phishing remains so prevalent is the availability of leaked email addresses. In 2021, there was an average of 16.5 leaked emails per 100 internet users, with nearly 1 billion emails exposed globally. These breached databases are often sold on dark web marketplaces, where cybercriminals purchase email addresses to use in phishing attacks. With such easy access to personal information, cybercriminals can launch widespread phishing campaigns with minimal effort.
Once a phishing attack is successful, the consequences can be severe. Victims may face financial loss, damage to personal or professional reputations, and prolonged identity theft. For businesses, the stakes are even higher, as phishing can lead to data breaches, regulatory penalties, and a loss of customer trust.
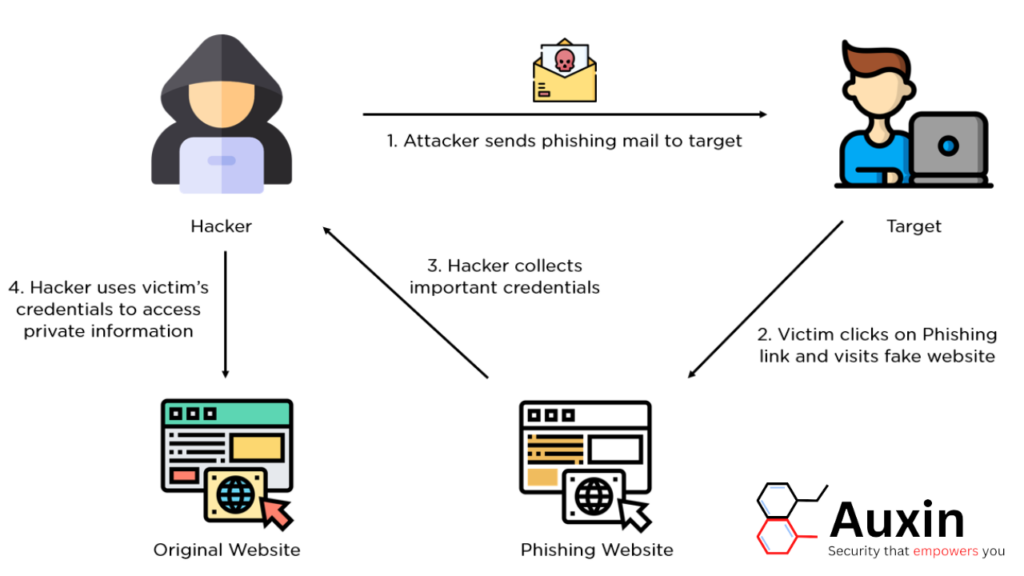
Protecting Yourself and Your Business from Phishing
According to Auxin Security, it is essential for both individuals and businesses to take proactive steps to protect themselves. Here are some practical tips to stay safe:
- Be cautious with emails and messages: Always double-check the sender’s email address and be suspicious of unsolicited messages asking for personal information. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or unverified sources.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security, such as MFA, helps prevent unauthorized access to your accounts even if your login credentials are compromised.
- Update your passwords regularly: Use strong, unique passwords for each account and change them frequently. Consider using a password manager to help manage them securely.
- Educate your employees: Businesses should provide regular training to employees on recognizing phishing attempts and the importance of cybersecurity best practices.
- Invest in security software: Using up-to-date antivirus software, email filters, and firewalls can help prevent phishing attacks from reaching your inbox or devices.
- Report phishing attempts: If you receive a suspicious message, report it to the appropriate authorities or platforms to help prevent others from falling victim to the same scam.
How Auxin Security Can Help
At Auxin Security, we specialize in helping businesses strengthen their defenses against phishing and other cyber threats. Our comprehensive cybersecurity solutions include advanced email filtering, threat detection systems, and tailored employee training to ensure your team is prepared to spot and respond to phishing attempts. We also offer cutting-edge tools to monitor and protect your digital assets, preventing data breaches and securing sensitive information. With our expertise in DevSecOps, cloud security, and AI-driven threat detection, Auxin Security provides a multi-layered approach to safeguarding your organization from cybercrime. Let us help you build a resilient security framework that protects your business and your customers from the growing threat of phishing.






